Java 注解的解析有两种方式:反射和注释处理器(APT/JSR 269)。
本文主要介绍通过反射来解析注解,它是在运行时解析的,所以反射要求注解必须是 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 类型的。在 .class 文件和 JVM 中都会保留注解信息,运行时才能通过反射来获取并解析注解。但是反射比较慢,所以需要考虑效率问题。
注解体系
所有的注解都是 Annotation 的子接口,类中所有的元素都是 AnnotatedElement 的实现。
源码分析
1 | // 所有注解的父接口 |
类图结构
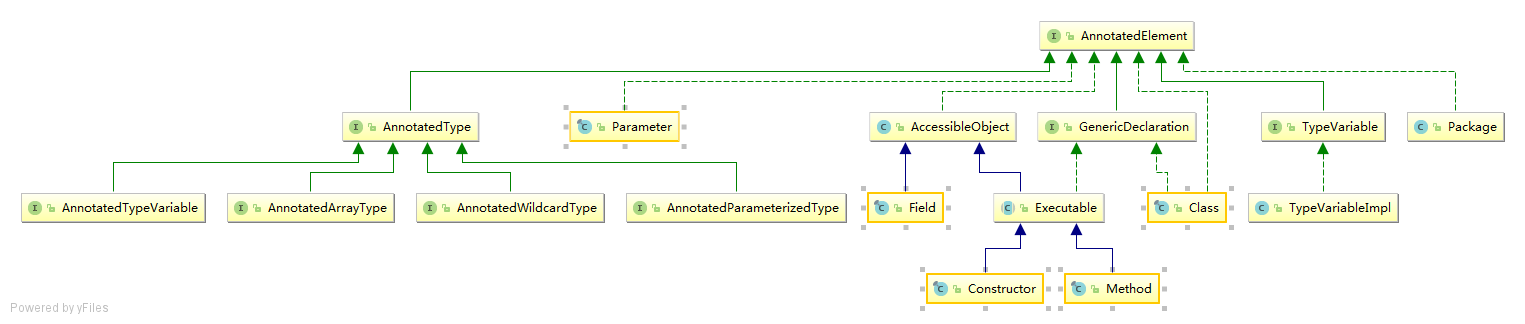
注解的本质
注解的位置只能放到类型前面,不能放到变量名,方法名之前。
注解是接口
注解使用关键字 @interface 来表示,实际上它也的确是接口。
1 | (RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) |
BindView 用来注解字段,并且在运行时也保留了注解信息。反编译结果如下:
1 | xmt@server005:~/annotation$ javap -v -c BindView.class |
反编译后发现所有的注解实际是接口,并且继承了 Annotation。所以使用反射解析注解时,可以使用父接口 Annotation 来表示任意注解类型。
注解在 class 文件中
自定义注解如果标注为 CLASS, RUNTIME,表示会在 class 文件中保留注解信息。
1 | public class TestAnnotation{ |
测试类中使用 @BindView 注解整型变量 i,反编译结果:
1 | xmt@server005:~/annotation$ javap -v -c TestAnnotation |
反编译后发现,变量 i 中保留了一个 RuntimeVisibleAnnotations 标记。后续反射解析时,就是通过这个标记来获取相关注解的。
AnnotatedType 体系介绍
AnnotatedType 体系是 Java 8 新加的,是泛型 Type 体系对应的被注解类型。AnnotatedType 既能获取被注解元素的类型,也能获取该元素上的注解数组。示例:@CustomAnnotation("value") CustomClass
AnnotatedType.getType
被注解元素的类型,即CustomClass。AnnotatedElement.getAnnotations
该元素上的注解数组,即{CustomAnnotation}。
AnnotatedType 类型并不是一定会有注解,只是代表拥有被注解的能力。比如 int i ,AnnotatedType 仅仅代表整型 int,而它并没有被注解。
源码分析
1 | // 被注解类型 |
示例
1 | // 声明了两个类型变量 S, T,其中 S 的边界是多限定 |
反射解析注解
动态代理
反射解析注解都使用的是动态代理技术访问注解的键值对,解析类源码文件:AnnotationParser.java, AnnotationInvocationHandler.java
1 | public class AnnotationParser { |
测试代码打印反射获取的 Annotation 类类型:
1 | // 测试代码 |
从输出结果可以看出,反射获取的 Annotation 类类型都是动态代理生成新类的类名。
常规解析
被注解的的类:
1 | ( |
注解反射解析:
1 | public class TestAnnotationParsingReflect { |
AnnotatedType 体系解析
AnnotatedType 是 Java 8 新增加强型注解,可以注解到任意代码位置,如下示例为解析 TestGenericAnnotation 类中的所有注解。
1 | public class TestGenericAnnotationParsingReflect { |